Check hard drive read/write speed on CentOS 8 with dd command
To evaluate the performance of a server, in addition to CPU and RAM configuration, you need to pay attention to another important parameter, which is the read/write speed or I/O (input/output) speed of the hard drive.
The following article will guide you to Check hard drive read/write speed on Centos 8 with dd command
What is hard drive read/write speed?
Hard drive read/write speed is a measure of performance on a storage device, which is the speed of reading and writing data of a drive in real-life usage situations.
In addition to storing data, the hard drive is also directly related to important issues when using a computer such as: computer startup speed, computer data export speed, or any operations on your computer such as copying, cutting and pasting, starting software, … fast or slow depends on whether the hard drive read/write speed is good or not.
Why do you need to know the speed of your hard drive?
In addition to a powerful CPU and RAM, your computer also needs a hard drive with a read-write speed that meets the system’s read-write needs to run smoothly. Suppose the CPU has finished processing a process and requests to write the processed data to the hard drive before continuing the next process. With a slow write speed, the entire system is inevitably “delayed”.
Benefits of checking the read and write speed of a hard drive
Checking the read and write speed of a hard drive is an important process to evaluate the performance and stability of a hard drive in a computer or other data storage device. Here are some important benefits of performing this test:
- Performance evaluation: Speed testing allows you to evaluate the data processing ability of the hard drive. By knowing the read and write speed, you can evaluate whether the hard drive meets the requirements of the job.
- Storage Management: Checking the read and write speeds also helps you evaluate the speed at which data can be copied and moved to and from your hard drive. This is useful when you want to back up data or move large files.
- Detect problems and errors: If the read and write speeds do not meet the hard drive’s specifications, there may be a hardware or operating system problem.
- Optimize performance: By checking the speed, you can identify factors that can increase or decrease the performance of your hard drive.
- Ensure reliability: If the hard drive performs consistently during the test, it indicates that the hard drive is working well and there are no issues to worry about.
So how to check hard drive speed, the article below will guide you to check hard drive read/write speed on CentOS 8 with dd command
Check hard drive read/write speed on CentOS 8 with dd command
Use dd – the simplest command to test hard drive speed.
– At the terminal, go to the folder mounted on the hard drive, here is the /mnt folder
# cd /mnt
– Run the following command and wait a moment to get the result:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=test01 bs=1M count=1024
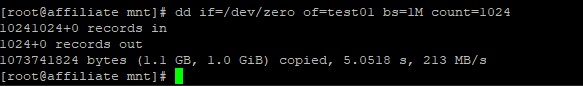
We can see the write speed displayed in the 3rd line of results, that speed is the hard drive write speed, The dd command successfully copied 1 GB of data from /dev/zero to test01 in 5.0518 seconds, for an average speed of 213 MB/s.
Or we can use the following command to check the speed at which data has been completely written to the physical disk:
# dd if=/dev/zero of=test01 bs=1M count=1024 conv=fdatasync
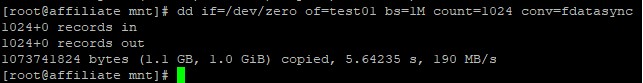
The conv=fdatasync parameter tells dd to write the data to disk and wait until all data is finish executing, bypassing the buffer.
This result shows that the drive’s write speed is 190 MB/s when required to write the entire 1 GB of data directly to the disk, including synchronization time to ensure the data is actually written.
- The average write speed of an HDD (mechanical hard drive) is usually around 50–150 MB/s, depending on the type of drive and year of manufacture. With newer HDDs or high-speed HDDs (7200 RPM or higher), the speed can reach around 100 MB/s or higher. If the HDD speed is below 50 MB/s, the performance will probably be slow and may need to be check or upgrade.
- SSDs (solid state drives) have much higher write speeds than HDDs. For SATA SSDs (common), the average write speed is usually around 200–550 MB/s. NVMe SSDs can reach speeds from 1000 MB/s to several thousand MB/s, depending on the version and quality of the drive.
Speed rating:
- HDDs above 50 MB/s are usable normally; above 100 MB/s is good performance for HDDs.
SSDs above 200 MB/s are the baseline performance; above 500 MB/s is good for SATA SSDs, while NVMe SSDs can reach above 1000 MB/s.
Note: These numbers are sequential write speeds, which are good for copying large files. With small files, speeds may drop due to processing delays.
Conclusion
Checking the read/write speed of a hard drive on CentOS 8 with the dd command is very important to evaluate performance and choose a suitable hard drive. Through the testing process, you will better understand the data processing capacity and performance of the hard drive. This helps you make smart decisions when choosing to buy a new hard drive or optimize the performance of your server.
If you have any questions about Linux/Windows VPS service, please contact us for advice and register for a free VPS account.