0%
Cheap Windows VPS
Looking for Cheap Windows VPS with fast deployment and powerful performance? At DaintyCloud, we offer Windows VPS solutions for Server editions (2012, 2016, 2019, 2022) – ready to launch instantly with full administrator access. Whether you’re an individual, developer, or business, our Windows VPS delivers speed, reliability, and flexibility you can count on.

Explore our cheap VPS services with high speed, stable operation, outstanding performance
We don't just offer cheap Windows VPS, Linux VPS — we provide enterprise-grade infrastructure optimized for speed, uptime, and user experience. With instant setup and full administrator access, you can get started in minutes.
Whether you use it for remote desktop, applications or resource-intensive tasks, our VPS ensures smooth performance. We always aim for the satisfaction of every user.
0%
0%
Instant Windows VPS deployment with worldwide locations
Our platform allows you to deploy a Windows VPS instantly with just a few clicks. No long setup times or technical delays – launch, connect, and start working immediately.
Deploy multiple high-performance servers in multiple countries simultaneously, with full administration directly from the web interface.
Easy administration with full tools: Restart server, power off, renew package, reinstall operating system, and set up auto-renewal.

Ultra-Fast & Stable Network
Stable infrastructure with 100–1000Mbps speeds, supported by Tier III — high-performance data centers.
🔹 Reliable Connection Worldwide
Diverse Windows Versions
Supports Windows Server 2012–2022, pre-optimized for smooth performance.
🔹 Pre-Activated, Full Access

Global Infrastructure
Deploy high-performance VPS in 30+ countries with low latency and reliable bandwidth.
🔹 Optimized connectivity
Cheap VPS Window in the Americas Region
We support a comprehensive range of Windows operating systems, including Windows 11 with its modern interface and enhanced security, Windows 10 known for stability and widespread adoption, and server editions such as Windows Server 2022 (latest LTSC release), Windows Server 2019 (hybrid-ready, built on Windows 10), Windows Server 2016 (optimized for cloud integration), and Windows Server 2012 (based on Windows 8 for legacy support). All versions come pre-installed, pre-activated, and fully optimized for smooth performance and complete administrator control.
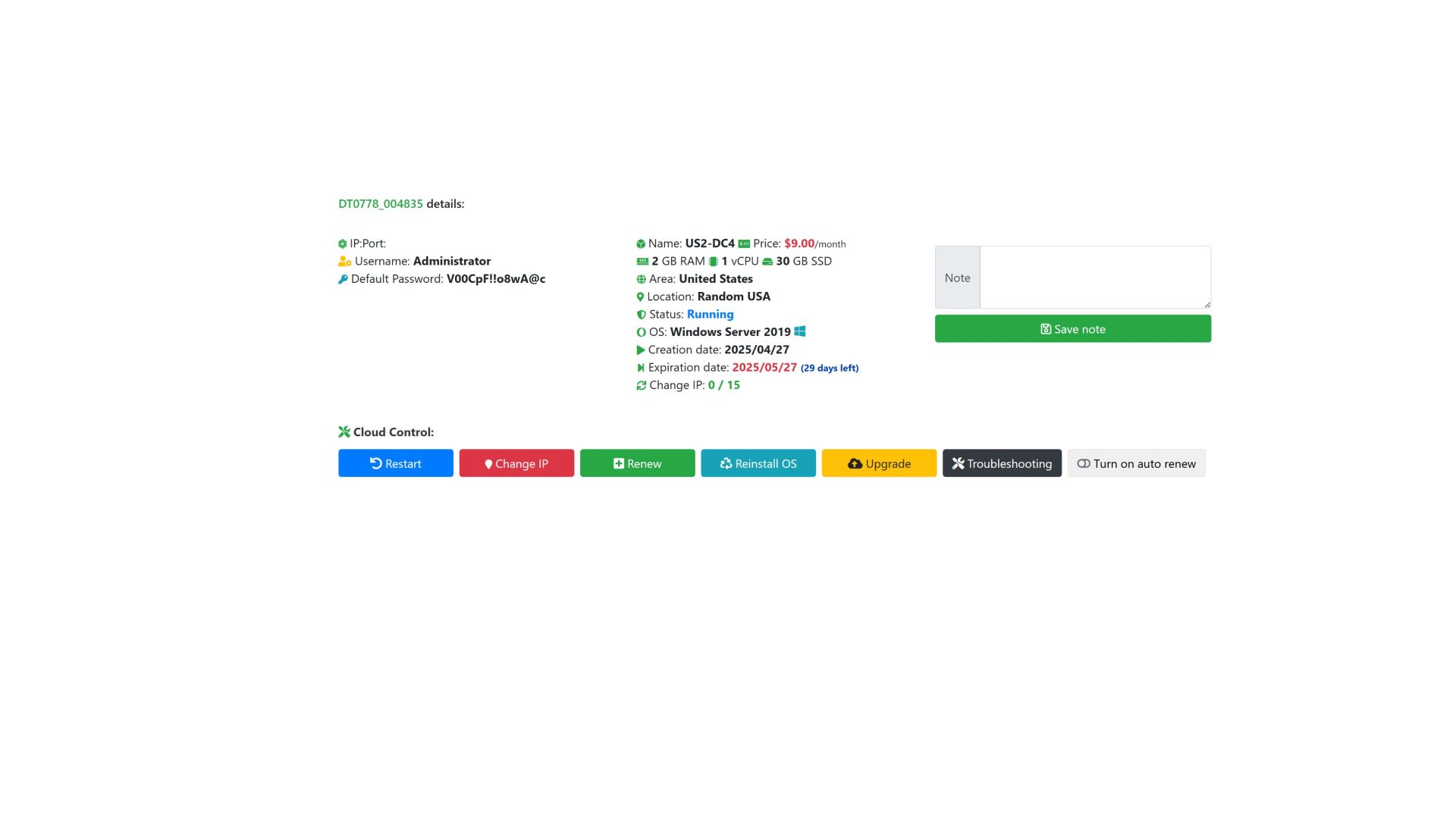
 United States Windows VPS
United States Windows VPS
United States & Other location: Canada, Argentina, Colombia, Chile, Brazil, Mexico
Ram
|
CPU
|
Storage
|
Port
|
Windows
|
Monthly
|
Deploy
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 7.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 9.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 2 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 11.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 2 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 17.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 4 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 23.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 4 vCPU | 60 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 33.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 39.0 | Deploy | |
| 16 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 56.0 | Deploy | |
| 32 GB | 16 vCPU | 240 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 68.0 | Deploy |
Cheap VPS Window in the Europe Region
We support a comprehensive range of Windows operating systems, including Windows 11 with its modern interface and enhanced security, Windows 10 known for stability and widespread adoption, and server editions such as Windows Server 2022 (latest LTSC release), Windows Server 2019 (hybrid-ready, built on Windows 10), Windows Server 2016 (optimized for cloud integration), and Windows Server 2012 (based on Windows 8 for legacy support). All versions come pre-installed, pre-activated, and fully optimized for smooth performance and complete administrator control.
 United Kingdom Windows VPS
United Kingdom Windows VPS
United Kingdom & Other location: Austria, Bulgaria, Denmark, Finland, Germany, France - 20+ countries
Ram
|
CPU
|
Storage
|
Port
|
Windows
|
Monthly
|
Deploy
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 8.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 10.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 2 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 12.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 2 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 18.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 4 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 25.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 4 vCPU | 60 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 33.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 45.0 | Deploy | |
| 16 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 56.0 | Deploy | |
| 32 GB | 16 vCPU | 240 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 78.0 | Deploy |
Cheap VPS Window in the Asia Region
We support a comprehensive range of Windows operating systems, including Windows 11 with its modern interface and enhanced security, Windows 10 known for stability and widespread adoption, and server editions such as Windows Server 2022 (latest LTSC release), Windows Server 2019 (hybrid-ready, built on Windows 10), Windows Server 2016 (optimized for cloud integration), and Windows Server 2012 (based on Windows 8 for legacy support). All versions come pre-installed, pre-activated, and fully optimized for smooth performance and complete administrator control.
 Singapore Windows VPS
Singapore Windows VPS
Singapore & Other location: Japan, Korea, Taiwan, Philippines - 10+ countries
Ram
|
CPU
|
Storage
|
Port
|
Windows
|
Monthly
|
Deploy
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 8.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 10.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 2 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 12.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 2 vCPU | 50 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 18.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 4 vCPU | 50 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 25.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 4 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 33.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 45.0 | Deploy | |
| 16 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 56.0 | Deploy | |
| 32 GB | 12 vCPU | 240 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 105.0 | Deploy |
Cheap VPS Window in the Middle East and Africa Region
We support a comprehensive range of Windows operating systems, including Windows 11 with its modern interface and enhanced security, Windows 10 known for stability and widespread adoption, and server editions such as Windows Server 2022 (latest LTSC release), Windows Server 2019 (hybrid-ready, built on Windows 10), Windows Server 2016 (optimized for cloud integration), and Windows Server 2012 (based on Windows 8 for legacy support). All versions come pre-installed, pre-activated, and fully optimized for smooth performance and complete administrator control.
 South Africa Windows VPS
South Africa Windows VPS
South Africa & Other location: Egypt, Dubai, Oman, Iraq- 4+ countries
Ram
|
CPU
|
Storage
|
Port
|
Windows
|
Monthly
|
Deploy
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 GB | 1 vCPU | 25 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 9.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 1 vCPU | 50 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 18.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 2 vCPU | 60 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 27.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 2 vCPU | 100 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 36.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 4 vCPU | 180 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 72.0 | Deploy | |
| 12 GB | 4 vCPU | 260 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 108.0 | Deploy | |
| 16 GB | 8 vCPU | 350 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 144.0 | Deploy | |
| 24 GB | 12 vCPU | 500 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 216.0 | Deploy |
Cheap VPS Window in the Australia Region
We support a comprehensive range of Windows operating systems, including Windows 11 with its modern interface and enhanced security, Windows 10 known for stability and widespread adoption, and server editions such as Windows Server 2022 (latest LTSC release), Windows Server 2019 (hybrid-ready, built on Windows 10), Windows Server 2016 (optimized for cloud integration), and Windows Server 2012 (based on Windows 8 for legacy support). All versions come pre-installed, pre-activated, and fully optimized for smooth performance and complete administrator control.
 Australia Windows VPS
Australia Windows VPS
Australia
Ram
|
CPU
|
Storage
|
Port
|
Windows
|
Monthly
|
Deploy
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 8.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 1 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 10.0 | Deploy | |
| 2 GB | 2 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 12.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 2 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 18.0 | Deploy | |
| 4 GB | 4 vCPU | 30 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 25.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 4 vCPU | 60 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 33.0 | Deploy | |
| 8 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 45.0 | Deploy | |
| 16 GB | 8 vCPU | 90 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 56.0 | Deploy | |
| 32 GB | 12 vCPU | 240 GB | 100-1000Mbps | $ 105.0 | Deploy |
One-Click Deploy & Full Administrator
Fast and PowerfulQuick Initialization
Quick initialization and full VPS administration on the webiste.
Full Control Panel
You can reinstall your operating system, restart your VPS and much more on your admin panel.
Easy to use
The login process is convenient and simple, supported on both mobile and computer.
Easy upgrade
Upgrade quickly and easily with just a few simple steps on the web interface.
Cheap GPU VPS
Cheap GPU VPS for Gaming, Android Emulator or video processing. Starting from $96 monthly.



Contact Us
- Dedicated Sales Team
- 24/7 Customer Support
- Dedicated Technical Team
- 24/7 Technical Support







 United States Windows VPS
United States Windows VPS 
 Our office address: 29A International Business Park, Singapore 609934
Our office address: 29A International Business Park, Singapore 609934  +61 452 331 613
+61 452 331 613  Contact Mail
Contact Mail